Overview
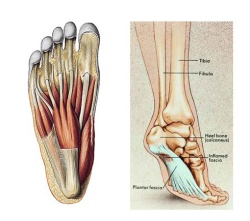
Plantar fasciitis, also called “heel pain syndrome,” affects approximately 2 million people in the United States each year. Plantar fasciitis can come on gradually as the result of a degenerative process or sudden foot trauma. It can appear in one heel or both. It is generally worse on taking the first few steps in the morning or after prolonged sitting or non-weight-bearing movement. Symptoms can be aggravated by activity and prolonged weight bearing. Obesity, too, is hard on the feet-it can cause plantar pain or it can make that pain worse. The plantar fascia connects the calcaneal tubercle to the forefoot with five slips directed to each toe respectively. Other conditions, such as calcaneal fat pad atrophy, calcaneal stress fracture, nerve entrapment, and rheumatoid arthritis may also cause foot pain. These conditions may be found in combination with plantar fasciitis, or separate from it. A blood test can help pinpoint the cause(s).
Causes
Currently no single factor has been reliably identified as contributing to the development of plantar fasciitis. The two risk factors with the most support from current research. Decreased ankle dorsiflexion. Increased Body Mass Index (BMI) in non-athletic populations. These factors are related in that both lead to increased strain on the arch, both lead to increased compression on the heel. When dorsiflexion range of motion (ankle flexibility) is lacking, the body compensates by increasing movement of the arch. In this way, decreased ankle dorsiflexion influences pronation and places strain on the underside of the foot. Similarly, having a high BMI causes strain because it places a load on the foot that may be in excess of what the foot can support. As mentioned earlier, overpronation is thought to be a contributing factor, but studies on this have so far produced mixed results. The second way these factors relate to each other is in the way people stand. A lack of ankle flexibility and a high BMI can both cause increased pressure on the heel in standing. Keeping weight on the heels causes compression under the heel. But it also means the muscles and ligaments in the arch are not being used to balance your body weight. Lack of use, I suspect, is a greater danger than overuse. Looking beyond these potential contributors to heel pain though, there is one major factor that overshadows them all-the way footwear alters the normal function of the foot.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis is characterized by the following signs and symptoms. Acute plantar fasciitis, pain is usually worse in the morning but may improve when activity continues; if the plantar fasciitis is severe, activity will exacerbate the pain, pain will worsen during the day and may radiate to calf or forefoot, pain may be described anywhere from “minor pulling” sensation, to “burning”, or to “knife-like”, the plantar fascia may be taut or thickened, passive stretching of the plantar fascia or the patient standing on their toes may exacerbate symptoms, acute tenderness deep in the heel-pad along the insertion of the plantar aponeurosis at the medial calcaneal tuberosity and along the length of the plantar fascia, may have localized swelling. Chronic plantar fasciitis, plantar fasciitis is classified as “chronic” if it has not resolved after six months, pain occurs more distally along the aponeurosis and spreads into the Achilles tendon.
Diagnosis
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist is usually sufficient to diagnose plantar fasciitis. Occasionally, further investigations such as an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI may be required to assist with diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Non Surgical Treatment
Although there is no single cure, many treatments can be used to ease pain. In order to treat it effectively for the long-term, the cause of the condition must be corrected as well as treating the symptoms. Rest until it is not painful. It can be very difficult to rest the foot as most people will be on their feet during the day for work. A plantar fasciitis taping technique can help support the foot relieving pain and helping it rest. Plantar fasciitis tapingApply ice or cold therapy to help reduce pain and inflammation. Cold therapy can be applied for 10 minutes every hour if the injury is particularly painful for the first 24 to 48 hours. This can be reduced to 3 times a day as symptoms ease. Plantar fasciitis exercises can be done if pain allows, in particular stretching the fascia is an important part of treatment and prevention. Simply reducing pain and inflammation alone is unlikely to result in long term recovery. The fascia tightens up making the origin at the heel more susceptible to stress. Plantar fasciitis night splint. Plantar fasciitis night splint is an excellent product which is worn overnight and gently stretches the calf muscles preventing it from tightening up overnight.
Surgical Treatment
Plantar fasciotomy is often considered after conservative treatment has failed to resolve the issue after six months and is viewed as a last resort. Minimally invasive and endoscopic approaches to plantar fasciotomy exist but require a specialist who is familiar with certain equipment. Heel spur removal during plantar fasciotomy has not been found to improve the surgical outcome. Plantar heel pain may occur for multiple reasons and release of the lateral plantar nerve branch may be performed alongside the plantar fasciotomy in select cases. Possible complications of plantar fasciotomy include nerve injury, instability of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot, fracture of the calcaneus, prolonged recovery time, infection, rupture of the plantar fascia, and failure to improve the pain. Coblation (TOPAZ) surgery has recently been proposed as alternative surgical approaches for the treatment of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis.
Stretching Exercises
Calf stretch. Lean forward against a wall with one knee straight and the heel on the ground. Place the other leg in front, with the knee bent. To stretch the calf muscles and the heel cord, push your hips toward the wall in a controlled fashion. Hold the position for 10 seconds and relax. Repeat this exercise 20 times for each foot. A strong pull in the calf should be felt during the stretch. Plantar fascia stretch. This stretch is performed in the seated position. Cross your affected foot over the knee of your other leg. Grasp the toes of your painful foot and slowly pull them toward you in a controlled fashion. If it is difficult to reach your foot, wrap a towel around your big toe to help pull your toes toward you. Place your other hand along the plantar fascia. The fascia should feel like a tight band along the bottom of your foot when stretched. Hold the stretch for 10 seconds. Repeat it 20 times for each foot. This exercise is best done in the morning before standing or walking.

